Creep Analysis 3
The blog article of Creep Analysis 3 showed how Dr. Ghali et al. explained the creep analysis by flexibility methods.
To better understand the creep behavior, solve the previous example in a less efficient way. Here, different sign conventions will be applied.
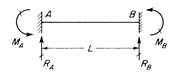
At time t0, the immediate displacements/rotations for member 1 due to uniform loads are

At time t1, the immediate displacements/rotations due to uniform loads at span 2 are (MIDAS file ex4.2A)

The signs in the table are according to the global axis. Converting into element local axis,

Restrained displacements/rotations are


Let

Restrained member end forces are

The remaining calculations are the same as the previous example.

He is a Senior Supervising Engineer with a high level of expertise in the design and analysis of suspension bridges. He has a solid fundamental understanding of structures and can apply his knowledge exceptionally well to the design and analysis of highly complex structures. He is also a strong communicator, able to identify and distill the key information that is relevant to the task at hand and present it in a clear and quickly understandable manner.

(Scheduled for an upcoming update)


![Design and Practical Examples of Baseplates and Anchor Rods [sample download]](https://2495902.fs1.hubspotusercontent-na1.net/hubfs/2495902/%EC%8D%B8%EB%84%A4%EC%9D%BC22.png)
![Understanding Drafting Standards [ Drawing download ]](https://2495902.fs1.hubspotusercontent-na1.net/hubfs/2495902/%EC%8D%B8%EB%84%A4%EC%9D%BC24.png)
![Key Changes in ACI 318-19: A New Standard for Structural Design [ PDF download]](https://2495902.fs1.hubspotusercontent-na1.net/hubfs/2495902/%EC%8D%B8%EB%84%A4%EC%9D%BC21-1.png)
![Design and Practical Examples of Lug design(ASME BTH-1) [sample download]](https://2495902.fs1.hubspotusercontent-na1.net/hubfs/2495902/%EC%8D%B8%EB%84%A4%EC%9D%BC20-1.png)